Appendix 6C. Transparency in arms transfers
I. Introduction
II. The United Nations Register of Conventional Arms
III. National and regional reports on arms exports
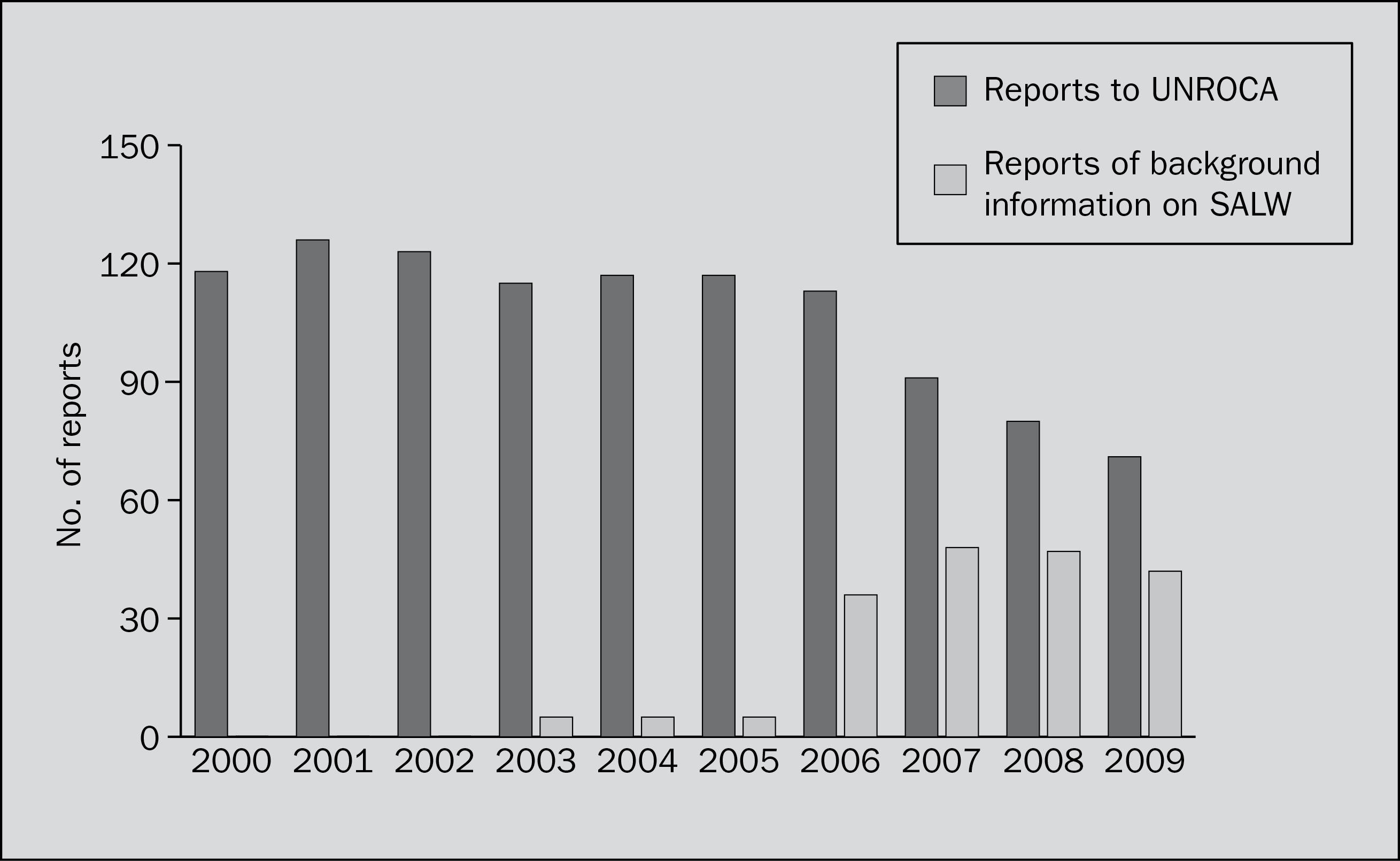
Figure 6C.1. Number of reports submitted to the United Nations Register of Conventional Arms, 2000–2009
Table 6C.1. Reports submitted to the United Nations Register of Conventional Arms, by region, 2005–2009
Table 6C.2. The timeliness of annual reports on arms exports for 2009
Table 6C.3. Submissions of information to the European Union annual report on arms exports, 2003–2009
Table 6C.4. States participating in international, regional and national reporting mechanisms on arms transfers, 2008–10
Appendix 6C describes the current status of existing mechanisms for international transparency in arms transfers [PDF].
Summary
Official and publicly accessible data on arms transfers is important for assessing states’ arms export and procurement policies. However, publishing data on arms sales and acquisitions is a sensitive issue for nearly all states.
The United Nations Register of Conventional Arms (UNROCA) is the key international mechanism of official transparency on arms transfers. The recent downward trend in states’ participation in UNROCA continued during 2010. Only 72 states submitted reports on their arms transfers during 2009, including 43 submissions of information on transfers of small arms and light weapons (SALW).
Since the early 1990s an increasing number of governments have published national reports on arms exports. As of January 2011, 34 states had published at least one national report on arms exports since 1990, and 30 have done so since 2008.
Reports to UNROCA, 2000–2009
Mark Bromley (United Kingdom) is a Researcher with the SIPRI Arms Transfers Programme.
Dr Paul Holtom (United Kingdom) is the Director of the SIPRI Arms Transfers Programme.